Python 内存管理
引用和对象
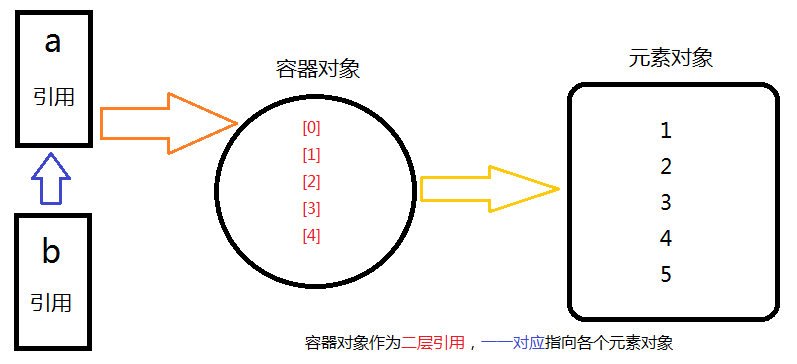 * python 会缓冲短字符串和小整数对象(-5 ~ 256),多个引用会引用同一个对象
* python 不会缓冲场字符串、容器、其他对象
* python 会缓冲短字符串和小整数对象(-5 ~ 256),多个引用会引用同一个对象
* python 不会缓冲场字符串、容器、其他对象
对象
typedef struct_object{
int ob_refcnt;
struct_typeobject *ob_type;
}PyObject;
- ob_refcnt:引用计数
- ob_type:类型的类型(元类型 metatype)
对象引用计数
sys.getrefcount()
- sys.getrefcount() 调用时因为 getrefcount() 也会增加引用,所以结果会比实际 ref count 大 1
GC
>>> import gc
>>> gc.get_threshold()
(700, 10, 10)
代际和 GC: * 0 代:年轻代,对应 get_threshold() 第 1 项(700) * 当 “新分配的对象(object allocation) - 释放的对象(object deallocation)” 大于 700 时触发 0 代扫描 * 当引用计数为 0 时放入 1 代 * 1 代:中年代,对应 get_threshold() 第 2 项(10) * 当 0 代进行了 10 次扫描时触发扫描 * 当引用计数为 0 时放入 2 代 * 2 代:老年代,对应 get_threshold() 第 3 项(10) * 当 1 代进行了 10 次扫描时出发扫描 * 当引用技术为 0 释放
手动触发 GC
>>> result = gc.collect()
>>> print(result)
5
内存池机制
内存管理空间结构
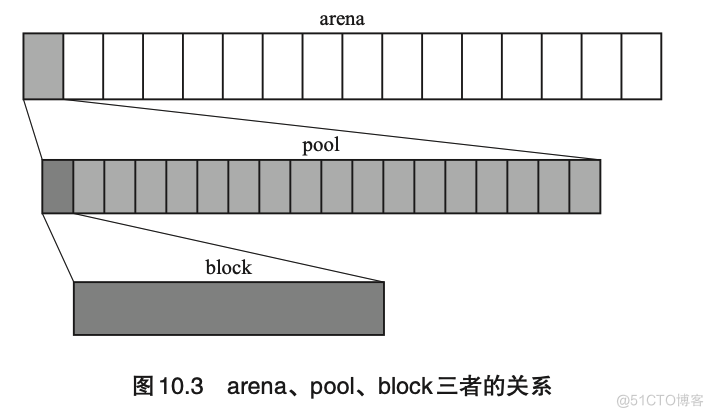
- arena
- pool
- block
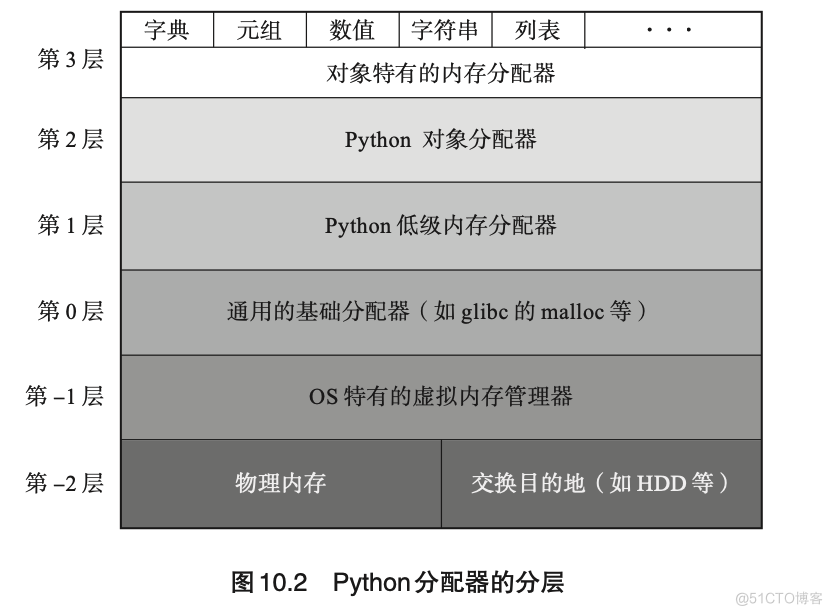
分层
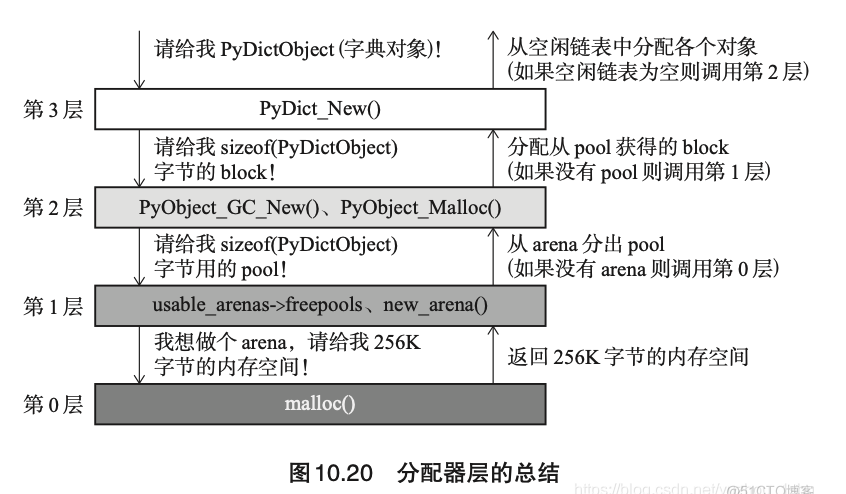
分配调用栈:

第 0 层
对接 OS 分配 python 所需内存
第 1 层
- 管理 arena
- arena 大小 256 KB
第 2 层
- 管理 pool 和 block
- pool 大小 4 KB
- block 小于 4 KB
- block 状态:
- 已分配
- 使用完毕
- 未使用
第 3 层
- 管理 python 对象使用的内存
